‘Five themes of geography‘ divides our information into five general categories: location, place, human environment interaction, movement, and region.
Human Environmental Interaction can be described as the connections between human beings and the entire ecological unit.
The human social systems and environment are intricate adaptive systems. They are intricate since ecological units and human social systems have a lot of elements and correlations between them. The adaptiveness is because of the feedback systems that support survival in continuously changing surroundings.
Human environment interaction is the way people adapt and modify the environment.
There are 3 types of human-environment interaction:
- The way people depend on the environment for food, water, timber, natural gas, etc.
- The way people adapt to the environment to fulfill their own needs
- The way people modify the environment positively or negatively, like drilling holes, building dams
The following explanations are notable examples of different kinds of human-environment interactions.
Examples of Different Kinds of Human-Environment Interactions
Some of these examples include:
1. The Use of Natural Resources

People use different kinds of natural reserves like timber, metals, and oil in their everyday lives. There is also a dependence on food and water for a continued existence. People also require energy for various reasons, such as cooking at home and industrial purposes.
Still, clothes, transport services, buildings, electronic devices, and other used items all need different resources to be produced.
The demand for natural resources keeps increasing with population growth, and utilization per individual rises with socio-economic advancement. Exhaustion of natural resources through extraction and exploitation is particularly a worry for resources that cannot be renewed.
2. Deforestation
One exacting predicament that is a result of too much misuse of natural resources and an illustration of human-environmental interaction is deforestation. It happens when forests get cut down, and the trees are not replaced or permitted to grow back.
Countries such as Ethiopia, Mexico, Brazil, America, Congo, and India have cleared many of their forests for economic and agricultural purposes to meet the food demand, fuel, and building materials. These activities have led to a steady loss of areas with forests, and it still continues.
Deforestation has a lot of unwanted results. For instance, forests are home to different species of trees, plants, and various animals, from small insects to birds, mammals, and reptiles. Hence, destroying them for agricultural or other human-centered interests greatly affects the ecosystem and may throw off its balance.
Plus, converting forests to agricultural areas decreases biodiversity, which is essential for human beings since they use other living organisms to provide a number of requirements such as:
- Food: plants such as wheat, rice, and maize and animals such as fish, chicken, and cows are used as sources of food.
- Medication: Most of the traditional and modern-day medicine is extracted from plants and animals.
- Ecological processes: Plants and microorganisms play a vital role in sustaining both human life and the ecosystem. They provide clean air, purify water, break down waste, and prevent soil erosion.
Deforestation is a major contributor to soil erosion. Cutting trees leaves the land bare, increasing the probability of soil being carried away during the rainy seasons or in the event of strong winds.
3. Energy Resources
Using renewable or non-renewable sources, whether to power transport and communication systems, electrical equipment, homes, or even offices, demonstrates human-environmental interaction.
Fossil fuels, for example, have been the key ingredient in the world’s globalization, but since they cannot be renewed, the amount is eventually inadequate, and their usage is not sustainable in the long run. Because of its downside, burning fossil fuels is the major reason for climate modification.
There are a number of renewable energies that can be used instead of fossil fuels like wind power, hydroelectric power, and solar power that work by converting the wind’s, water’s, and sun’s energy into electricity respectively.
4. Oil and Gas Drilling

Humans extract oil and gas for a lot of uses. However, the extraction of oil and gas has a lot of negative effects on the ecosystem. Oil spills, in particular, result in significant economic consequences, disrupting transportation and harming wildlife. Plus, when birds are affected by oil spills, it hampers their ability to hunt for food, jeopardizing their survival.
Oil spills also pose a risk to human health by contaminating seafood, making it unsafe to eat. Offshore drilling produces waste materials that, when released into the water, can poison aquatic animals.
Additionally, the process of drilling for oil carries the constant risk of accidents and injuries, with many individuals having lost their lives due to storms and drilling incidents.
Of course, that’s not to forget that the main product from drilling, methane, also contributes to climate modification. This consequently causes global warming, a change that causes modifications in rainfall patterns, melting of glaciers, and an increase in sea levels.
5. Water Resources
The use of water resources highly signifies human-environmental interaction. Water has a lot of uses, from domestic to agricultural and in industrial processes. The relative quantities of the three groups differ in various parts of the universe.
However, agriculture generally uses the largest quantity of water, and its demand keeps surging. The rising demand for water is leading to unsustainable use of water sources.
Recycling of water means it gets replenished, but taking extreme quantities of water from water bodies for use, whether domestically, agricultural, or industrial, reduces the percentage of water accessible for present and upcoming generations.
Universally, withdrawals of water have tripled over the decades because of the growing populace and the rise in usage per individual.
6. Relationships Between Human Activities and The Surroundings
People start interrelating with the environment from the moment they are born. For instance, individuals have for years been chopping down trees to clear ground to plant crops for years. In doing so, the ecosystem gets modified.
On the other hand, the environment has an effect on the people as well. A perfect case in point is how individuals change clothes in response to the weather – either when it is cold or hot.
The other examples are environmental occurrences like floods, wildfires, drought, pollution, earthquakes, and tornadoes. They can cause the dislocation of families, harm, death, and destruction of homes.
Other natural occurrences like lightning and earthquakes destroy water, pipelines, and other transport systems, leading to pollution of water and inaccessibility to crucial public services.
7. Vehicle Production

It is obvious that cars enable people to move faster, travel longer distances, and easily access resources that would otherwise be out of their reach. Despite all that, we must acknowledge that cars have been changing the universe negatively.
You see, transportation services are responsible for over a third of the globe’s greenhouse gas emissions. Plus, they have significantly contributed to air pollution, one of the leading causes of death, killing about 800,000 people annually.
Of course, all that is not forgetting accidents caused by vehicles, which take over 1.1 million lives every year. And yes, constructing roads ends up destroying the ecological units.
In addition, there is a lot of noise pollution caused by vehicles. The noise ends up chasing numerous animals away from their natural habitat, thus putting them in danger of extinction.
8. Littering
Litter has a lot of negative effects. For instance, it can cause the interference of water paths. Dumping of plastics improperly causes them to flow towards water paths following heavy rainfall and gradually end up in drainage pipes and sewerways. Over time, this litter can clog filters in the pipes, leading to bursts and damage.
Additionally, litter provides hiding and breeding grounds for disease-carrying vectors, leading to increased vector populations and the spread of diseases to both animals and humans.
9. Graffiti and The Use of Aerosols
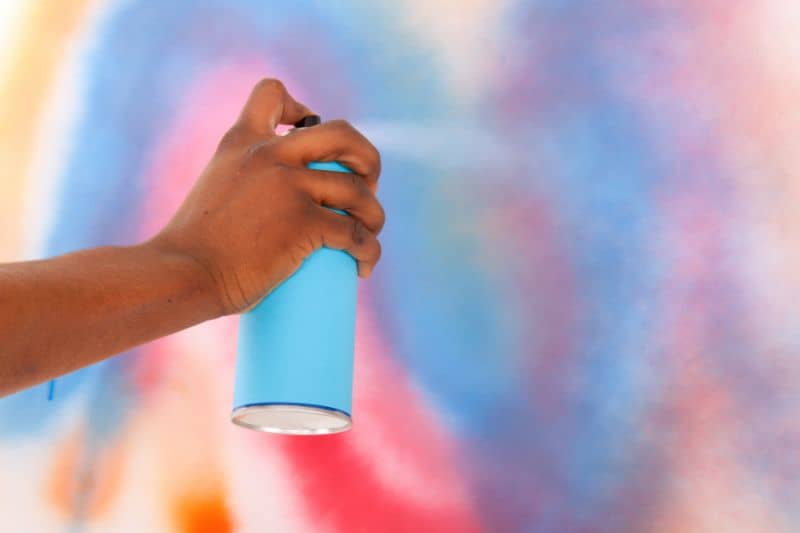
The use of graffiti and aerosols is poisonous to the environment and gives out fumes that get into the air, promoting global warming. Moreover, research has shown that Modern-day, CFC-free aerosol sprays also emit volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that add to ground-level ozone levels, a main ingredient that causes asthma.
Although modern-day paint is harmful to the environment, more often than not, the substances used to remove paint from the walls are exceedingly dangerous. There is a high probability of destroying the ecosystem when using and throwing away chemicals that are used in graffiti.






